Google and Tesla Accelerate the Expansion of the Robotics Industry
Recently, Google and Tesla announced large-scale investments in the humanoid robot industry, rapidly advancing the commercialization of robotics technology. Tesla is researching the development of the humanoid robot “Optimus” to directly perform tasks in factories, while Google is accelerating the integration of artificial intelligence and robotics technology by investing up to $675 million (approximately 9 trillion KRW) in the humanoid robot startup “Figure AI.” With global companies such as NVIDIA and Microsoft also entering this industry, the potential applications of robots are expanding significantly.
These large-scale investments are not just future prospects but moves aimed at transforming actual business and industrial structures. Tesla is developing robotic solutions that integrate production automation and autonomous driving technology beyond its existing electric vehicle and energy businesses, while Google is exploring ways to enable robots to learn independently and collaborate naturally with humans by leveraging its AI technology. This represents a decisive trend that could usher in an era where robots coexist with humans, moving beyond the concept of merely using robots as tools.
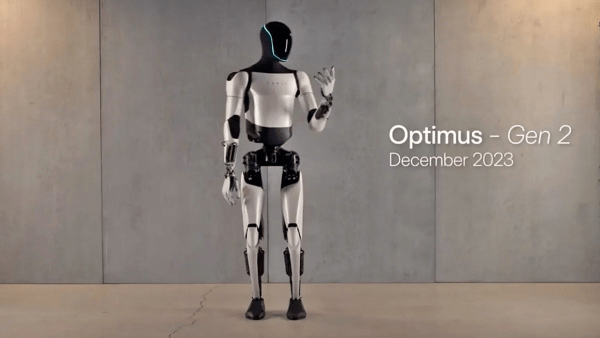
How Far Have Humanoid Robots Come?
The possibility of humanoid robots being fully integrated into daily life and industries is increasing. Robots are moving beyond simple assembly tasks in factories to roles in logistics, healthcare, legal analysis, and corporate management.
For example, some companies are already utilizing AI systems as tools to assist in managerial decision-making. In the financial and investment industries, AI-based analysis systems aid executives by processing data and creating predictive models, with an increasing number of companies incorporating AI into strategic planning. This trend highlights how AI is expanding its role from merely supporting administrative tasks to actively analyzing data and assisting in strategic decision-making.
Additionally, some biotech companies are adopting experimental robots to accelerate drug development. By automating numerous repetitive experiments previously conducted manually by researchers, robots are reducing the time required to develop new drug candidates, potentially bringing about innovation in the medical industry.
However, robotics technology still has limitations. While Tesla’s Optimus robot can walk and carry objects, it lacks the flexibility of human movements and struggles to adapt immediately to complex environments. Moreover, its ability to express emotions and engage in natural conversation remains at a rudimentary stage, making it unrealistic to expect human-like interactions. This suggests that robots are more likely to play a supportive role in specific tasks rather than fully replacing humans.
Although robots can be efficiently utilized in logistics and manufacturing, human roles remain crucial in service industries and creative professions. Emotional empathy and intuitive problem-solving are still areas where humans hold a significant advantage over robots. This raises important questions about how roles between robots and humans will be adjusted in the future.

Will Robots Become Our New Work Partners?
Despite these technological limitations, it is undeniable that robots are increasingly working alongside humans. AI robots that recognize facial expressions to assess user emotions and legal robots that analyze legal documents and assist in drafting contracts are emerging, gradually expanding the scope of robotic roles.
The pace of robot adoption is accelerating in industrial settings, particularly in high-risk jobs and roles requiring repetitive labor, where robots are increasingly replacing human workers. In Japan and Germany, robots are already being actively introduced into manufacturing industries to maximize productivity, aiming not just to replace labor but to establish autonomous work systems combined with artificial intelligence.
Additionally, recent studies have been conducted on robots learning human language patterns to perform customer service roles. Some companies are testing systems that combine AI chatbots with actual humanoid robots to replace call center operations, with research focused on analyzing customers’ voice tones and speech patterns to enable more natural responses.
Considering the large-scale investments and rapid technological advancements led by companies like Tesla and Google, the likelihood of working alongside robots in the future is increasing. However, rather than entirely replacing human labor, this trend is more likely to create a new working environment where humans and robots collaborate by leveraging their respective strengths.
Are we truly ready to accept robots as colleagues? Or is the moment approaching when technology surpasses us?
Keywords: Robotics Technology, Humanoid Robots, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Google, Tesla, Robotics Industry, AI Innovation, Automation, Future Technology, AI Robots